Current Ratio Definition, Explanation, Formula, Example and Interpretation
Therefore, this compensation may impact how, where and in what order products appear within listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products. Other factors, such as our own proprietary website rules and whether a product is offered in your area or at your self-selected credit score range, can also impact how and where products appear on this site. While we strive to provide a wide range of offers, Bankrate does not include information about every financial or credit product or service. However, similar to the example we used above, special circumstances can negatively affect the current ratio in a healthy company. For instance, imagine Company XYZ, which has a large receivable that is unlikely to be collected or excess inventory that may be obsolete. Both circumstances could reduce the current ratio at least temporarily.
Current Ratio Explained With Formula and Examples
It’s limited to only current debt and asset and short-term needs. I always teach my students to never believe in a penny stock. But 99% of these companies likely won’t even exist in a few years. Every Sunday I send out a free weekly watchlist of the hottest stocks I’m watching. I often stress to my students to prepare before you risk your hard-earned money. Too many people are too lazy in this industry to put in the work to be successful.
Reduce current liabilities
- Various factors, such as changes in a company’s operations or economic conditions, can influence it.
- Too many people are too lazy in this industry to put in the work to be successful.
- Be sure also to visit the Sortino ratio calculator that indicates the return of an investment considering its risk.
- When I plan to hold overnight, I tend to check more fundamentals.
- The current ratio of such entities significantly alters as the volume and frequency of their trade move up and down.
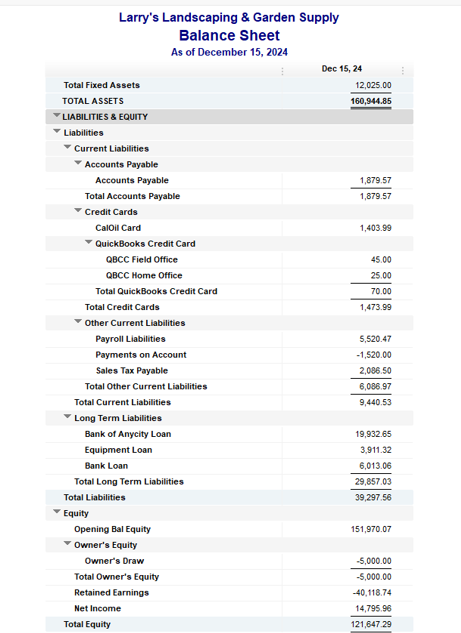
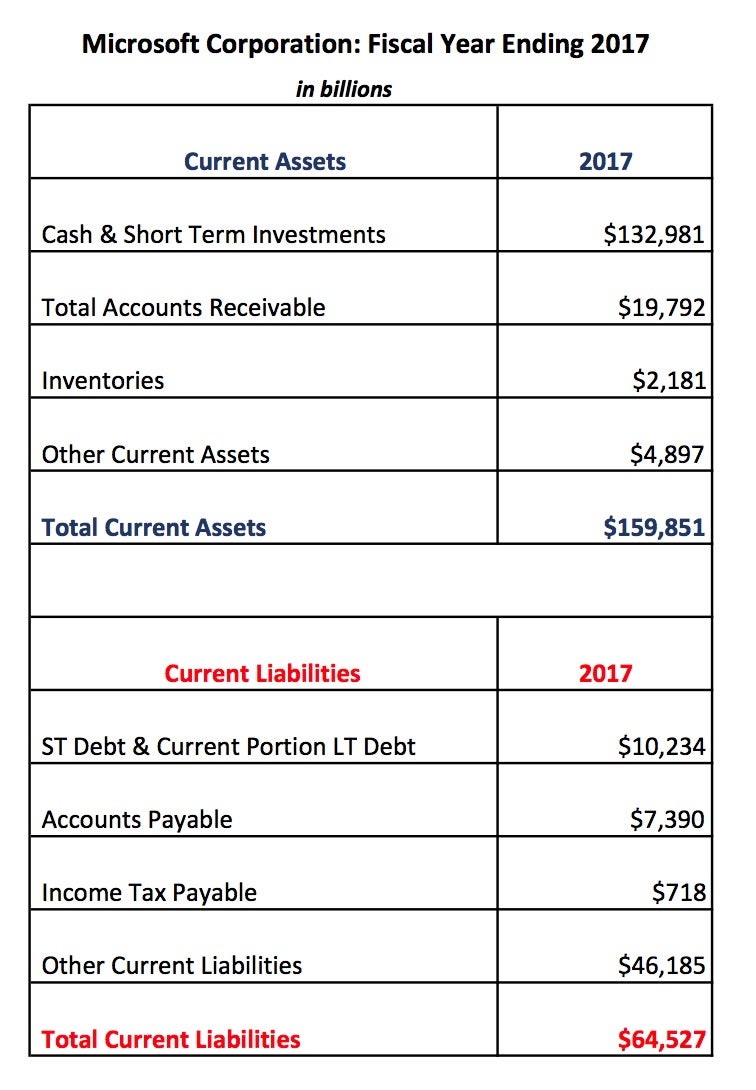
The current ratio is 2.75 which means the company’s currents assets are 2.75 times more than its current liabilities. A high current ratio is generally considered a favorable sign for the company. Creditors are more willing to extend credit to those who can show that they have the resources to pay obligations. However, a current ratio that is too high might indicate that the company is missing out on more rewarding opportunities.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
Over-trading companies are likely to face substantial difficulties in meeting their day-to-day obligations. We are an independent, advertising-supported comparison service. Find the best trucking accounting software for your business with our comparison guide. Read about features, pricing, and more to make the best decision for your company.
A current ratio that is in line with the industry average or slightly higher is generally considered acceptable. A current ratio that is lower than the industry average may indicate a higher risk of distress or default by the company. If a company has a very high current ratio compared with its peer group, it indicates that management may not be using its assets efficiently.
Accounting Services
Learn the skills you need for a career in finance with Forage’s free accounting virtual experience programs. And if you thought that was easy, try using the StocksToTrade software. This is an all-in-one trading platform that I helped create. I was sick of using so many websites to find the information I needed. StocksToTrade has everything you need in one place, even ratios. But it’s good to understand how it works and what it could mean.
The calculator will then provide you with the trends and a graph using your financial year on year metrics. A ratio greater than 1 means that the company has sufficient current assets to pay off short-term liabilities. So it is always wise to compare the obtained current ratio to that of other companies in the same branch of industry.
The trend is also more stable, with all the values being relatively close together and no sudden jumps or increases from year to year. An investor or analyst looking at this trend over time would conclude that the company’s the difference between fixed cost and variable cost finances are likely more stable, too. Though they may appear to have the same level of risk, analysts would have different expectations for each company depending on how the current ratio of each had changed over time.
